Jan 15, 18Introduction Interleukin‐23 (IL‐23), a member of the IL‐12 cytokine family, is a heterodimeric cytokine, which consists of an IL‐12p40 subunit, shared with IL‐12, and an IL‐23 specific p19 subunit 1The receptor for IL‐23 consists of IL‐23Rα in complex with IL‐12Rβ1, which also serves as a subunit for the IL‐12 receptor 2Nov 17, 17Interleukin‐23 (IL‐23), a member of the IL‐12 cytokine family, is a heterodimeric cytokine, which consists of an IL‐12p40 subunit, shared with IL‐12, and an IL‐23 specific p19 subunit 1 The receptor for IL‐23 consists of IL‐23Rα in complex with IL‐12Rβ1, which also serves as a subunit for the IL‐12 receptor 2Homeostatic IL23 receptor signaling limits Th17 response through IL22–mediated containment of commensal microbiota Author Shih, Vincent FengSheng, Cox, IL23 drives IL22 production to reinforce mucosal barrier function and elicit antimicrobial activities, and it also drives the differentiation of Th17 cells in an attempt to combat
Il 23 Signaling Regulation Of Pro Inflammatory T Cell Migration Uncovered By Phosphoproteomics
Il-23 receptor signaling
Il-23 receptor signaling-May 13, 21The IL23 receptor (IL23R) signaling pathway has pleiotropic effects on the differentiation of osteoclasts and osteoblasts, since it can inhibit or stimulate these processes via different pathwaysNov 01, 11Interleukin23 (IL23) is known to play a crucial role in the development and maintenance of T helper 17 cells It has been previously demonstrated that IL17 is involved in experimental Lyme




The Role Of Il 23 Receptor Signaling In Inflammation Mediated Erosive Autoimmune Arthritis And Bone Remodeling Razawy 18 European Journal Of Immunology Wiley Online Library
IL23R IL23R FACS analysis by Parham et al (02) readily detected binding of IL23, but not IL12, to IL23R Signal transduction analysis showed constitutive association of IL23R with JAK2 and liganddependent association with STAT3 (), as well as IL23dependent tyrosine phosphorylation of IL23RNov 17, 17Increasing evidence suggests that the IL‐23 signaling pathway may be involved in the development of autoimmunity and erosive joint damage IL‐23 can act either directly or indirectly on bone forming osteoblasts as well as on bone resorbing osteoclastsDec 22, INTERLEUKIN 23 RECEPTOR;
May 06, 21May 06, 21Homeostatic IL23 receptor signaling limits Th17 response through IL22mediated containment of commensal microbiota Characterization of potent IL23R smallpeptide modulator, 2305 (teeeqqly), that decreases inflammatory response Although they share a common subunit, IL23 and IL12 receptors are not expressed on the same cell populationsThe functional IL23 receptor complex consists of two receptor subunits, the IL12 receptor beta 1 subunit (IL12 R beta 1) and the IL23specific receptor subunit (IL23 R) (3) Human IL23 R cDNA encodes a 629 aa type I transmembrane protein with a 23 aa residue signal peptide, a 330 aa residue extracellular domain, a 23 aa residueOct 13, 11This study demonstrates that IL23R signaling is needed for B burgdorferiinduced IL17 production in vitro and that an IL23R gene SNP leads to impaired IL17 production However, the IL23R gene polymorphism is not crucial for the pathogenesis of chronic Lyme
IL23 signals through the IL23 receptor IL17producing T cells express IL23R, and IL23 plays an important role in sustaining Th17 cell responses in vivo Although one study showed loss of microRNAdependent regulation of one IBDassociated IL23R variant resulting in enhanced protein production, no enhanced IL23 levels have been found so far in AS ( Zwiers et al, 12 )IL23 signaling pathway IL23 plays important role in expanding and maintaining the Th17 cell population, a novel Tcell subset involved in antimicrobial immune response and establishment of many autoimmune diseases 1 IL23 receptor is composed of IL12RB1 and IL23R IL23R associates with JAK2 and in a liganddependent manner with STAT3 2The interleukin 23 (IL23) is a key proinflammatory cytokine in the development of chronic inflammatory diseases, such as psoriasis, inflammatory bowel diseases, multiple sclerosis, or rheumatoid arthritis The pathological consequences of excessive IL23 signaling have been linked to its ability to promote the production of inflammatory mediators, such as IL17, IL22,




Il 12 Family Signaling Pathways R D Systems
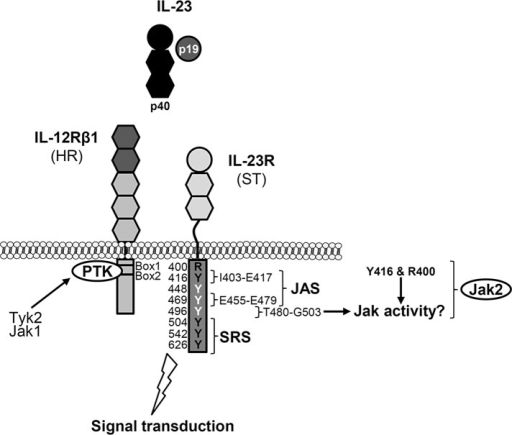



Overview Of Jak Binding Sites Within The Il 23 Receptor Open I
In contrast, IL23 signaling is involved in the stabilization and maintenance of Th17 cells, promotes memory T cell activation, and stimulates IL17mediated neutrophil recruitment to sites of infection Although these activities demonstrate that IL12 and IL23 induce different immune responses, both can be characterized as proinflammatoryIncreasing evidence suggests that the IL23 signaling pathway may be involved in the development of autoimmunity and erosive joint damage IL23 can act either directly or indirectly on bone forming osteoblasts as well as on bone resorbing osteoclastsIL23 functions in innate and adaptive immunity and may participate in acute response to infection in peripheral tissues IL23 may be responsible for autoimmune inflammatory diseases and be important for tumorigenesis Tissue specificity Expressed by
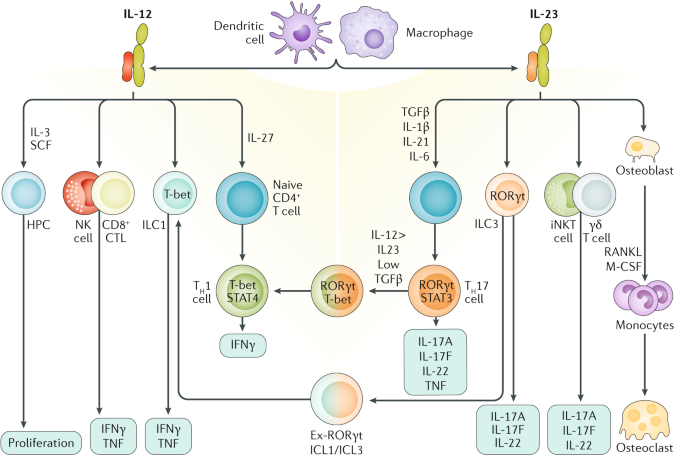



Il 12 Il 23 And Il 17 In Ibd Immunobiology And Therapeutic Targeting Nature Reviews Gastroenterology Hepatology




Il 23 Il 23r Signaling Induces Rort And Il 17 A Flow Cytometry Of Download Scientific Diagram
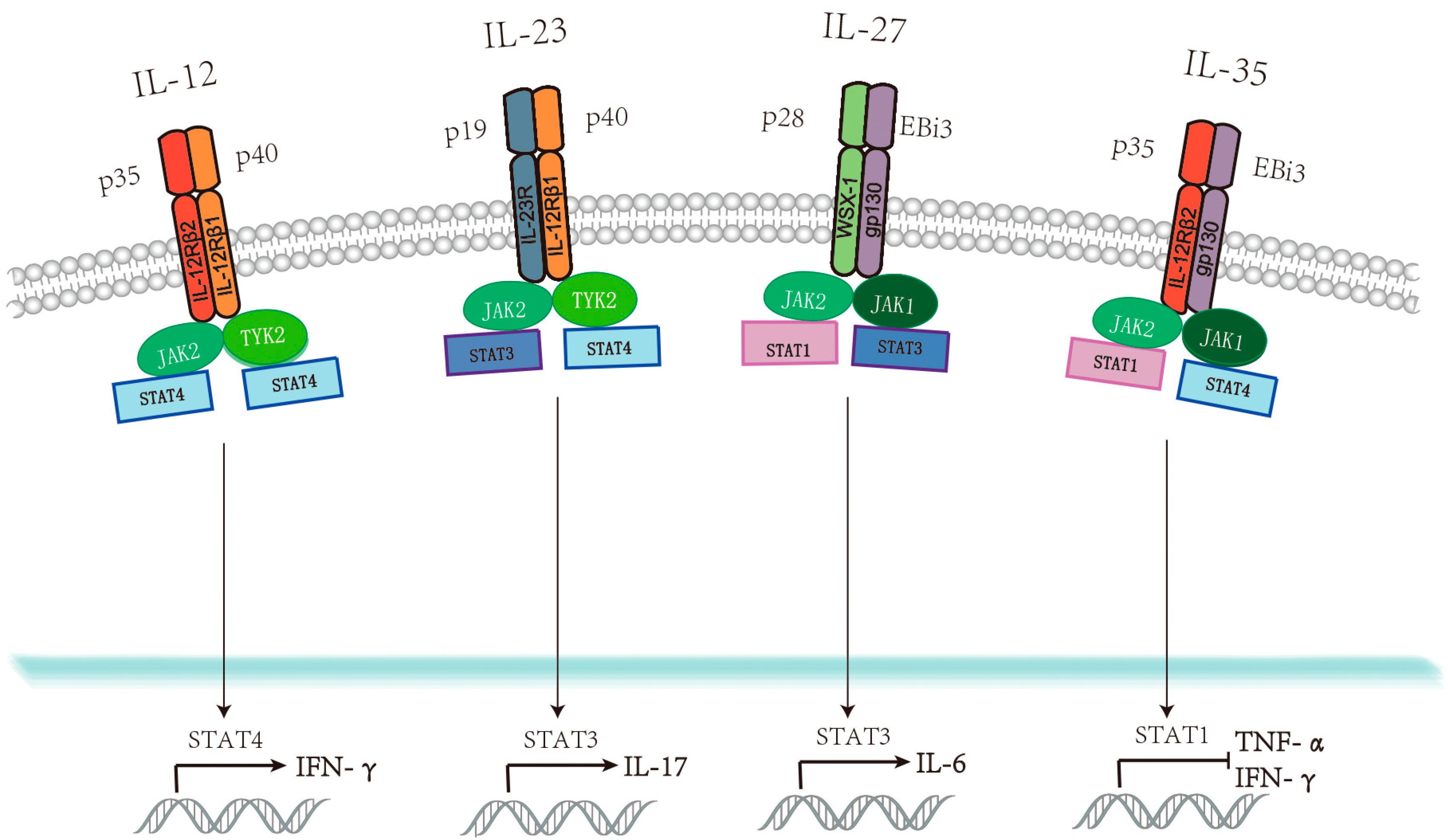
Feb 18, 21Feb 18, 21This extracellular receptor specificity is relayed to distinct patterns of intracellular signaling in which IL12 led to phosphorylation of STAT4 with minimal activation of STAT3 while IL23 led to phosphorylation of STAT3 without inducing STAT4 phosphorylation in primary human CD4 T cells (Figures 4B and 4C) The specificity of IL12 and IL23 signaling suggests that p40 plays similar roles in both complexes to recruit IL12Rβ1/Tyk2 and initiate STAT signalingBased on the shared role of the p40/IL12Rβ1 interaction in both the IL12 and IL23 receptor complexes, we targeted this interface to modulate STAT4 signaling in the context of IL12, and STAT3 signaling in the context of IL23, by systematically impairing theMar 23, IL23 receptor is associated with JAK2 and TYK2 that promote STAT3 phosphorylation and activation , and active STAT3 increases the expression of the transcription factor RORγt, which is crucial for IL17 production However, reported data suggest that in addition to the STAT3/RORγt axis, other IL23regulated events are involved in disease development
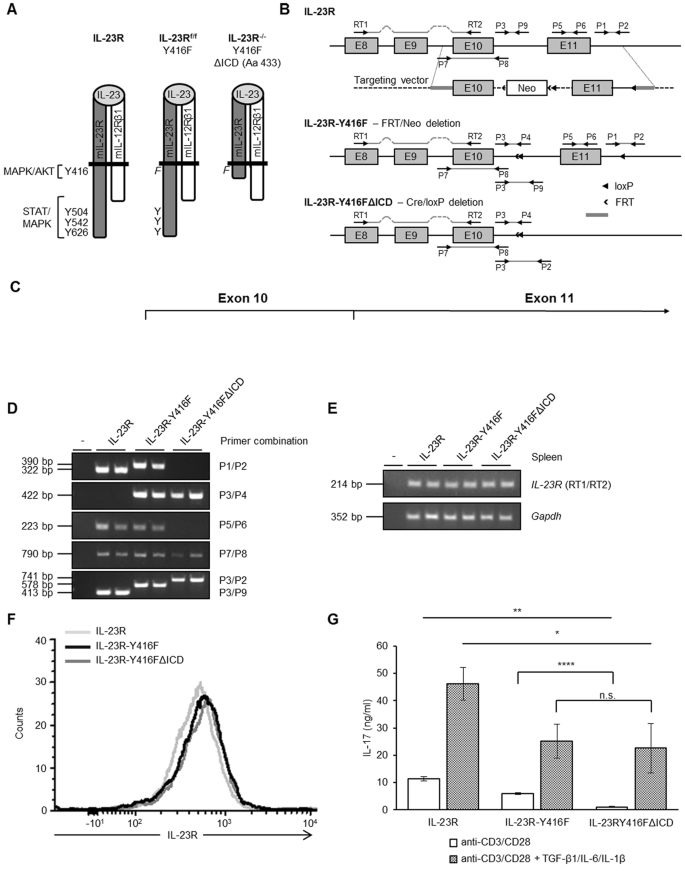



Il 23r Signaling Plays No Role In Myocardial Infarction Scientific Reports




Rbpj Controls Development Of Pathogenic Th17 Cells By Regulating Il 23 Receptor Expression Sciencedirect
Nov 02, 10Associates with IL12RB1 to form the interleukin23 receptor Binds IL23 and mediates Tcells, NK cells and possibly certain macrophage/myeloid cells stimulation probably through activation of the JakStat signaling cascade IL23 functions in innate and adaptive immunity and may participate in acute response to infection in peripheral tissuesHere, we demonstrate that the IL23 pathway dynamically regulates the abundance of SFB as well as mucosal barrier function in the adult animal Genetic or pharmacological inactivation of the pathway selectively perturbs the abundance of a small group of commensals, including SFB, and results in an impaired mucosal barrierMar 02, 21The human IL23 receptor rs A allele promotes the expression of a soluble IL23Rencoding mRNA species IL23R gene polymorphisms alone were not shown to be associated with AS in Iranian population;




A Receptor For The Heterodimeric Cytokine Il 23 Is Composed Of Il 12rb1 And A Novel Cytokine Receptor Subunit Il 23r The Journal Of Immunology
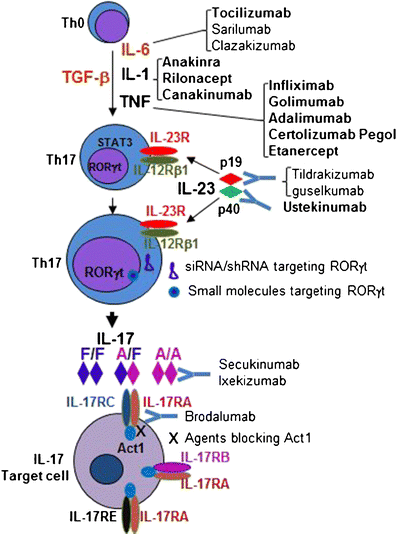



How Can We Manipulate The Il 23 Il 17 Axis Springerlink
We present a crystal structure of the quaternary IL23 (IL23p19/p40)/IL Interleukin12 (IL12) and IL23 are heterodimeric cytokines that are produced by antigenpresenting cells to regulate the activation and differentiation of lymphocytes, and they share IL12Rβ1 as aIt acts by binding to a receptor complex consisting of the IL12 receptor β1 (IL12Rβ1) and the IL23 receptor (IL23R) Upon binding, IL23 triggers a signaling pathway involving tyrosine kinase 2 (TyK2) and Janus kinase 2 (JAK2) leading to the activation of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3)The present invention relates to novel polypeptides that bind to IL23 receptor and inhibit the binding of IL23 to its corresponding receptor and cell signaling thereof The novel polypeptides of the present invention has a core structure of WX 1 X 2 X 3 W, where W is tryptophan, and X 1 , X 2 and X 3 are amino acids, with the proviso that when one of X 1 , X 2 or X 3 is W, the remaining



Frontiers Interleukin 22 Signaling In The Regulation Of Intestinal Health And Disease Cell And Developmental Biology




Il 23 A Cytokine That Acts On Memory T Cells Science Signaling
Homeostatic IL23 receptor signaling limits Th17 response through IL22–mediated containment of commensal microbiota Vincent FengSheng Shiha, Jennifer Coxa,1, Noelyn M Kljavinb, Hart S Denglera, Mike Reicheltc, Pawan Kumard, Linda Rangellc, Jay K Kollsd, Lauri Diehlc, Wenjun Ouyanga, and Nico Ghilardia,2 Departments of aImmunology, bMolecular Biology, andSummary of IL23R IL23R (interleukin 23 receptor) encodes for a protein this is required for IL23A signaling ( R ) Polymorphisms of this gene are associated with higher risk for Studies in animal models of multiple sclerosis showed that IL23 was responsible for the inflammation observed, not IL12 as previously thought Subsequently, IL23IL23 is a heterodimeric member of the IL12 family which shares the p40 subunit but contains a specific p19 subunit which can be recognized by the IL23 receptor Whereas IL6 and IL1β are necessary for induction of Th17 cells, IL23 is responsible for the maintenance of this T helper cell population and production of IL17 (1, 4, 18)



The Molecular Basis Of Chaperone Mediated Interleukin 23 Assembly Control Nature Communications



Viruses Free Full Text Immunoregulatory Functions Of The Il 12 Family Of Cytokines In Antiviral Systems Html
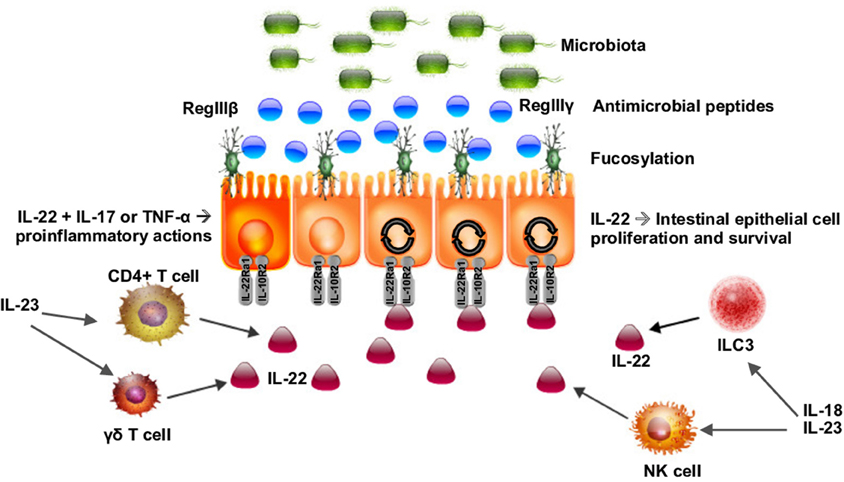
Oct 26, 16IL23 signals through its heterodimeric receptor (IL23R) that is composed of two subunits IL12Rβ1, which is shared by IL12 receptor complex, and IL23R, which is the unique subunit The p19 subunit of IL23 heterodimer interacts with IL23R, whereas the p40 subunit interacts with IL12Rβ1 chainSep 23, 14Homeostatic IL23 Receptor/IL22 Signaling Controls Intestinal SFB Colonization To assess if homeostatic IL23 expression is required to control the level of SFB colonization in the gut, we quantitated the abundance of bacteria species in Interleukin23 subunit p19 deficient ( IL23p19 −/− ) or IL23 receptor deficient ( IL23R −/− ) mice vs WT littermates by quantitativeIL23 is a heterodimer of p40 and p19 (which is related in structure to the p35 subunit of IL12) The p19 alone has no determined biological activity, but combines with p40 to form biologically active IL23 IL23 interacts with a receptor composed of the IL12Rβ1 subunit and the IL23specific subunit IL23R IL23 can activate similar signaling pathways as does IL12, although IL23




Overview Of Jak Binding Sites Within The Il 23 Receptor Complex Download Scientific Diagram




The Il 17 Family Of Cytokines In Health And Disease Abstract Europe Pmc
In addition, IL23 treatment significantly increased the accumulation of CD133 cells and activated the Wnt and Notch signaling pathways in CD133−IL23R ESCC cell lines Consistently, CD133−IL23R cells pretreated with IL23 showed stronger antiapoptosis activity when exposed to radiation and higher survival than untreated groupsRecently Dr Adamopoulos collaborated with Dr Savvides, a structural biologist at the VIB Insitute, Ghent in Belgium to further solve the structure of the IL23 and IL23 receptor complex BothWhile estradiol and progesterone increased IL17A production in Th17 cells by inhibiting Let7fmiRNA expression and increasing IL23 receptor (IL23R) expression, it remained unclear how estrogen signaling through the canonical nuclear receptors, estrogen receptor α (ERα) and/or ERβ, regulated this pathway




Jci Insight Il 23r Activated Stat3 Stat4 Is Essential For Th1 Th17 Mediated Cns Autoimmunity




Pdf Stat3 And Nf Kb Signal Pathway Is Required For Il 23 Mediated Il 17 Production In Spontaneous Arthritis Animal Model Il 1 Receptor Antagonist Deficient Mice1 Semantic Scholar
IL23 may constitute with IL17 an acute response to infection in peripheral tissues IL23 binds to a heterodimeric receptor complex composed of IL12RB1 and IL23R, activates the JakStat signaling cascade, stimulates memory rather than naive Tcells andFeb 01, 19IL23 and IL23 receptor signaling The cytokine IL23 was discovered in 00 when a novel p19 protein was described that interacts with the p40 protein subunit of IL12 to form a p19/p40 heterodimer 1 IL23 belongs to the IL12 cytokine family together with IL12 p35/p40, IL27 EBI3/p28 and IL35 EBI3/p35Sep 23, 14Homeostatic IL23 Receptor/IL22 Signaling Controls Intestinal SFB Colonization To assess if homeostatic IL23 expression is required to control the level of SFB colonization in the gut, we quantitated the abundance of bacteria species in Interleukin23 subunit p19 deficient (IL23p19 −/−) or IL23 receptor deficient (IL23R −/−) mice vs WT littermates by quantitative PCR




Profile Of Interleukin 22 In Gut Mucosal Health And Disease Ijicmr




Pdf Stat3 And Nf Kb Signal Pathway Is Required For Il 23 Mediated Il 17 Production In Spontaneous Arthritis Animal Model Il 1 Receptor Antagonist Deficient Mice1 Semantic Scholar
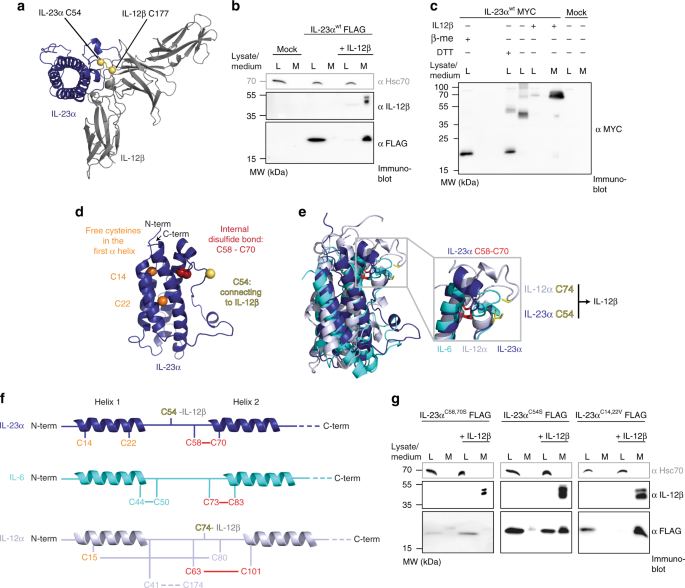
The IL23/IL23R/IL12Rbeta1 complex formation does not follow the classical site IIIIII architectural paradigmApr 01, Interleukin12 (IL12) and IL23 are heterodimeric cytokines that are produced by antigenpresenting cells to regulate the activation and differentiation of lymphocytes, and they share IL12Rβ1 as a receptor signaling subunitBackground/Purpose The interleukin (IL)23/IL17A immune pathway is critical for the development of autoimmune arthritis Systemic exposure of IL23 induced chronic arthritis, increased osteoclast differentiation and systemic bone loss in mice However, the role of IL23 on normal and pathologic bone remodeling is not fully elucidated Here we examined the role of IL23R signaling on bone




Il 23 Interleukin 23 Producing Conventional Dendritic Cells Control The Detrimental Il 17 Interleukin 17 Response In Stroke Stroke
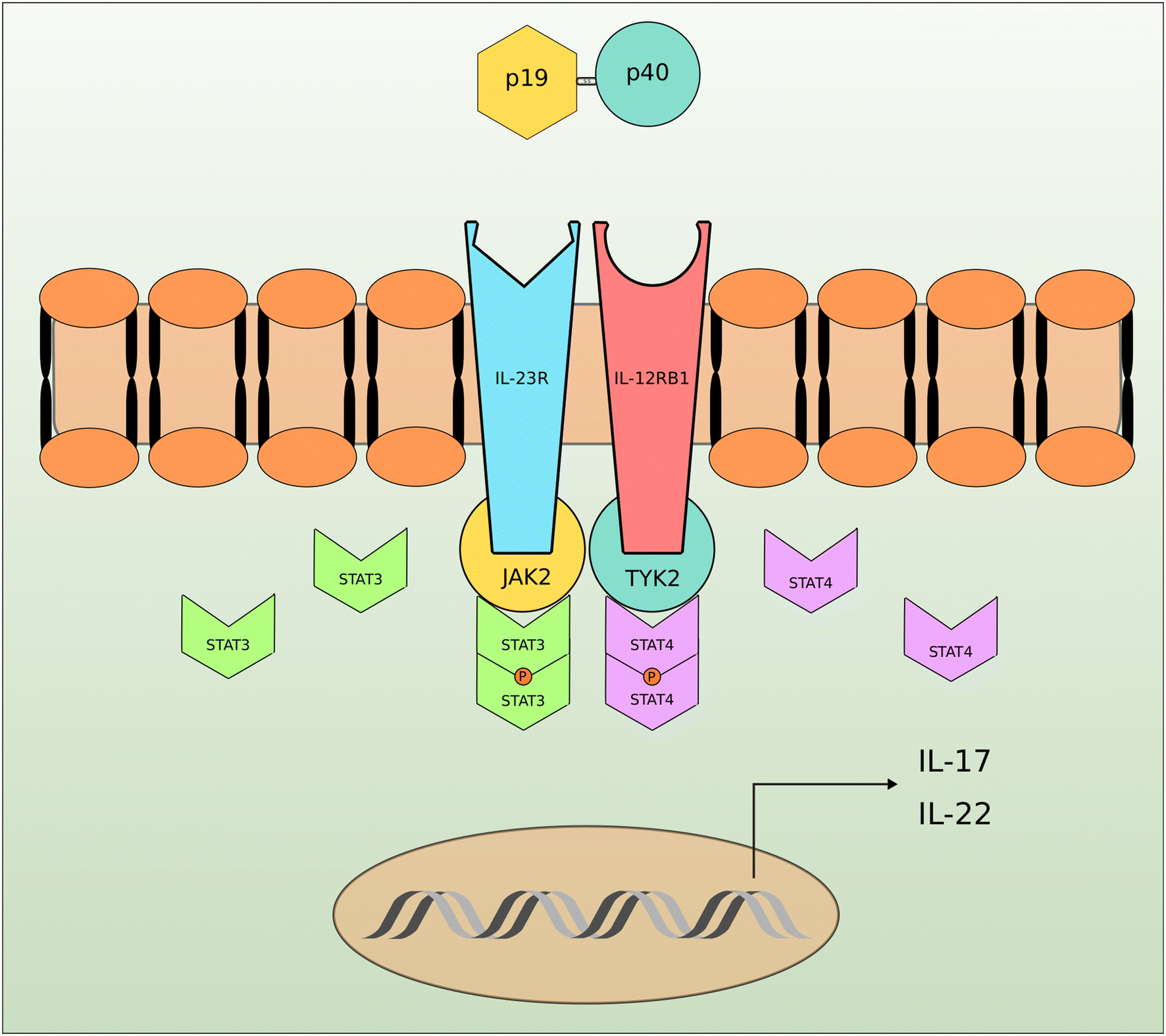



Figure 1 Interleukin 23 And Autoimmune Diseases Current And Possible Future Therapies Springerlink
Signaling via all of these receptors is mediated by members of the JakSTAT family Jak2 and either Jak1 or Tyk2 seem to mediate phosphorylation of STAT proteins associated with receptors for cytokines of the IL12 family IL12 mediates signaling via pSTAT4, IL23 mediates signaling via pSTAT3 and pSTAT4, IL27 mediates signaling via pSignificance Commensal microbiota are known to be required for the elicitation of host Th17 responses, which may mediate autoimmune diseases Here, we demonstrate that the IL23 pathway dynamically regulates the abundance of certain commensals and maintains barrier function Barrier disruption results in systemic dissemination of microbial products, which invokes the IL23Mar 13, IL23 plays a role in a signaling pathway that triggers inflammation IL23 inhibitors block the action of IL23, which can help limit the inflammation that




Il 12 Family Signaling Pathways R D Systems




Figure 1 From The Immunogenetics Of Psoriasis A Comprehensive Review Semantic Scholar
Jun , Up to10%cash backENZ and ODM Reduce Growth and Induce Cellular Senescence of AndrogenSensitive LNCaP and CastrationResistant C42 and 22Rv1 Cells To analyze the effect of IL23, first the presence of IL23 receptor (IL23R) was confirmed by Western blotting in both LNCaP and C42 cells (Fig 1a)The antibody recognizes three isoforms with the



Il 23 Signaling Regulation Of Pro Inflammatory T Cell Migration Uncovered By Phosphoproteomics



Il 23 Signaling Regulation Of Pro Inflammatory T Cell Migration Uncovered By Phosphoproteomics
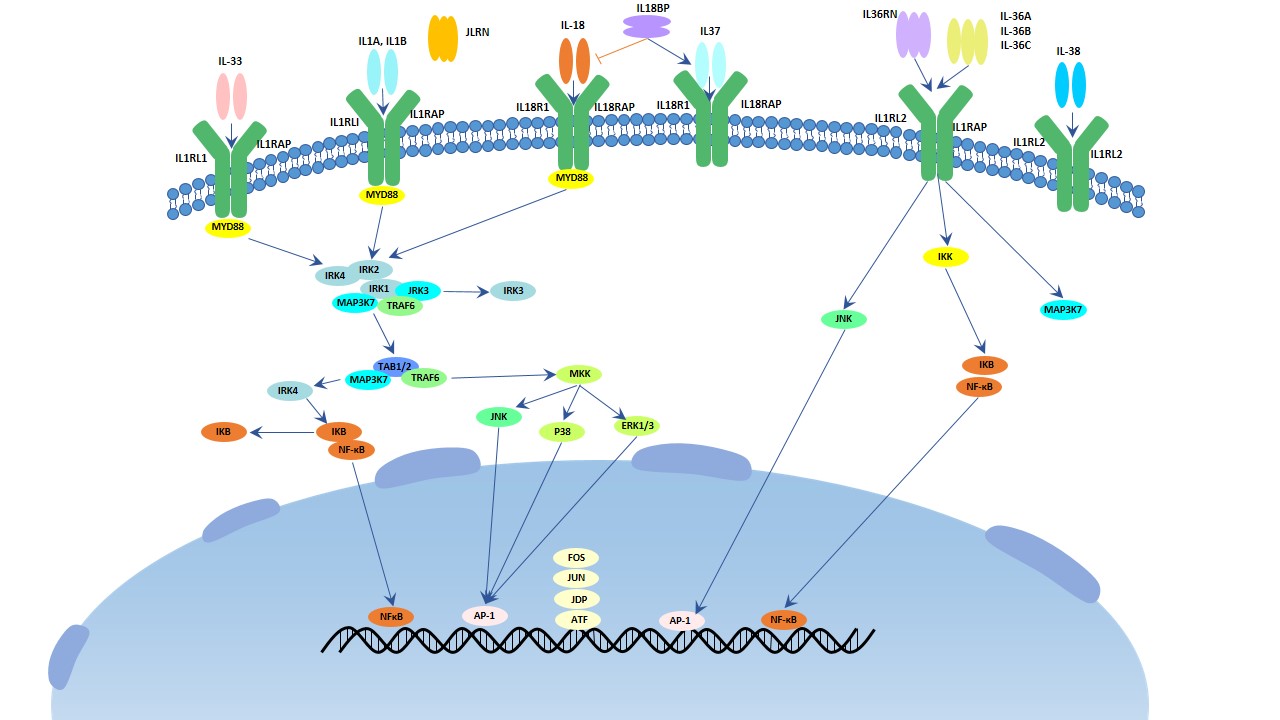



The Overview Of Interleukin




Il 23 Producing Il 10ra Deficient Gut Macrophages Elicit An Il 22 Driven Proinflammatory Epithelial Cell Response Science Immunology




Insights Into Il 23 Biology From Structure To Function Sciencedirect




Interleukin 23 Subunit Alpha Wikipedia




Interleukin 23 And Interleukin 17 Importance In Pathogenesis And Therapy Of Psoriasis




Signal Transduction Events Following Il 12 Il 23 Il 27 And Il 17 Download Scientific Diagram
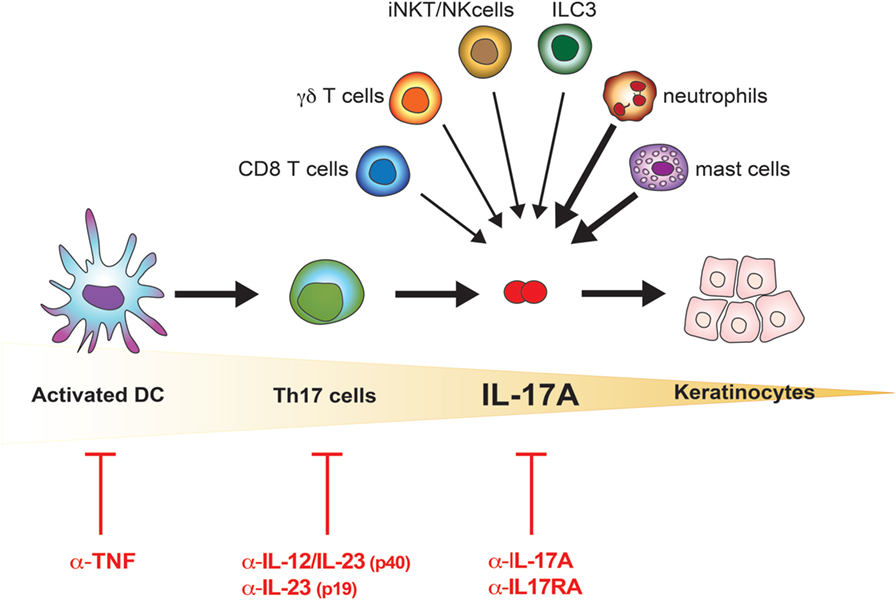



Frontiers The Il 17 Family Of Cytokines In Psoriasis Il 17a And Beyond Immunology
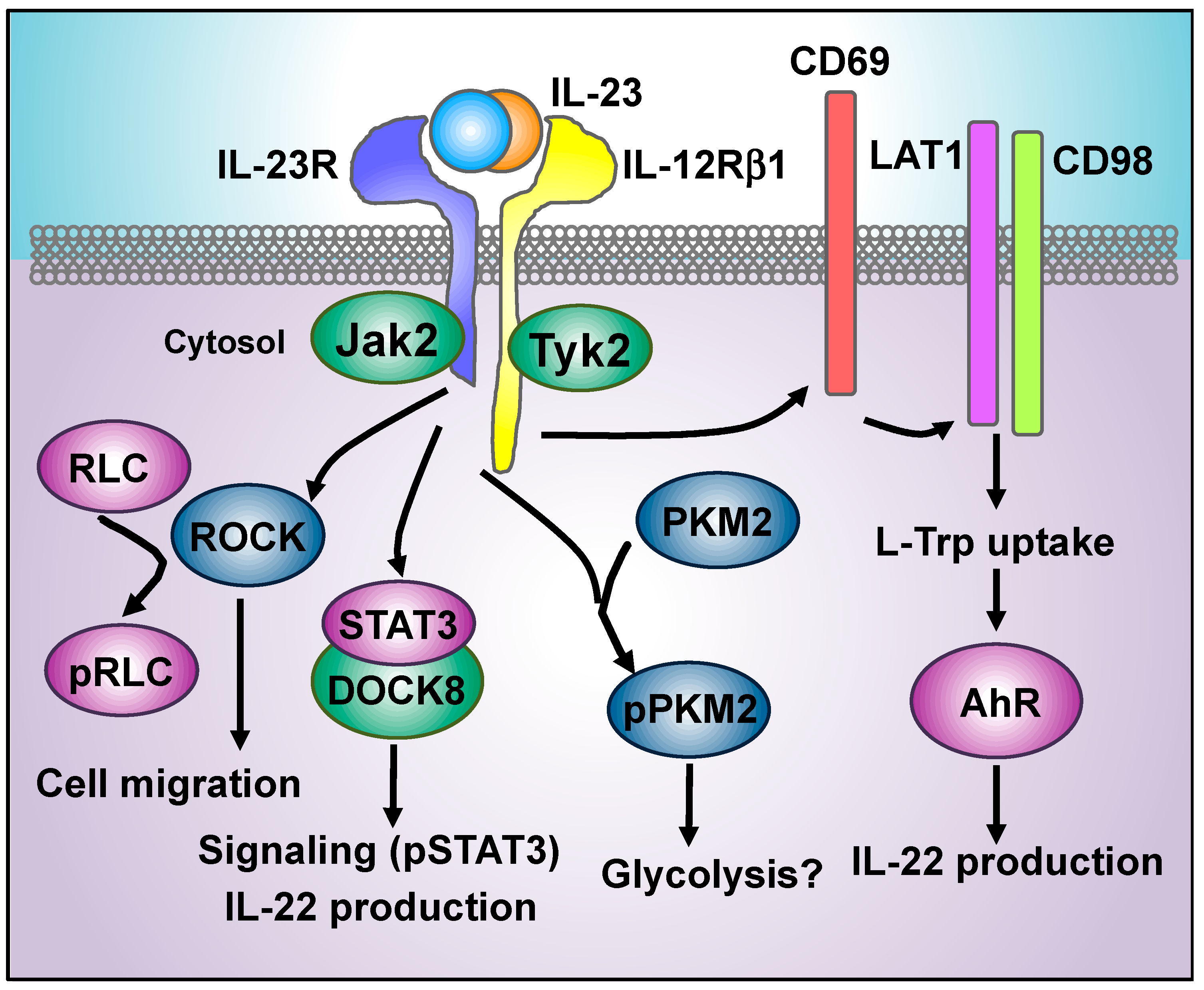



Cells Free Full Text Decoding Il 23 Signaling Cascade For New Therapeutic Opportunities Html




Interleukin 23 Subunit Alpha Wikipedia




Homeostatic Il 23 Receptor Signaling Limits Th17 Response Through Il 22 Mediated Containment Of Commensal Microbiota Pnas




Kegg Pathway C Type Lectin Receptor Signaling Pathway Mus Musculus Mouse




Stat3 And Nf Kb Signal Pathway Is Required For Il 23 Mediated Il 17 Production In Spontaneous Arthritis Animal Model Il 1 Receptor Antagonist Deficient Mice The Journal Of Immunology
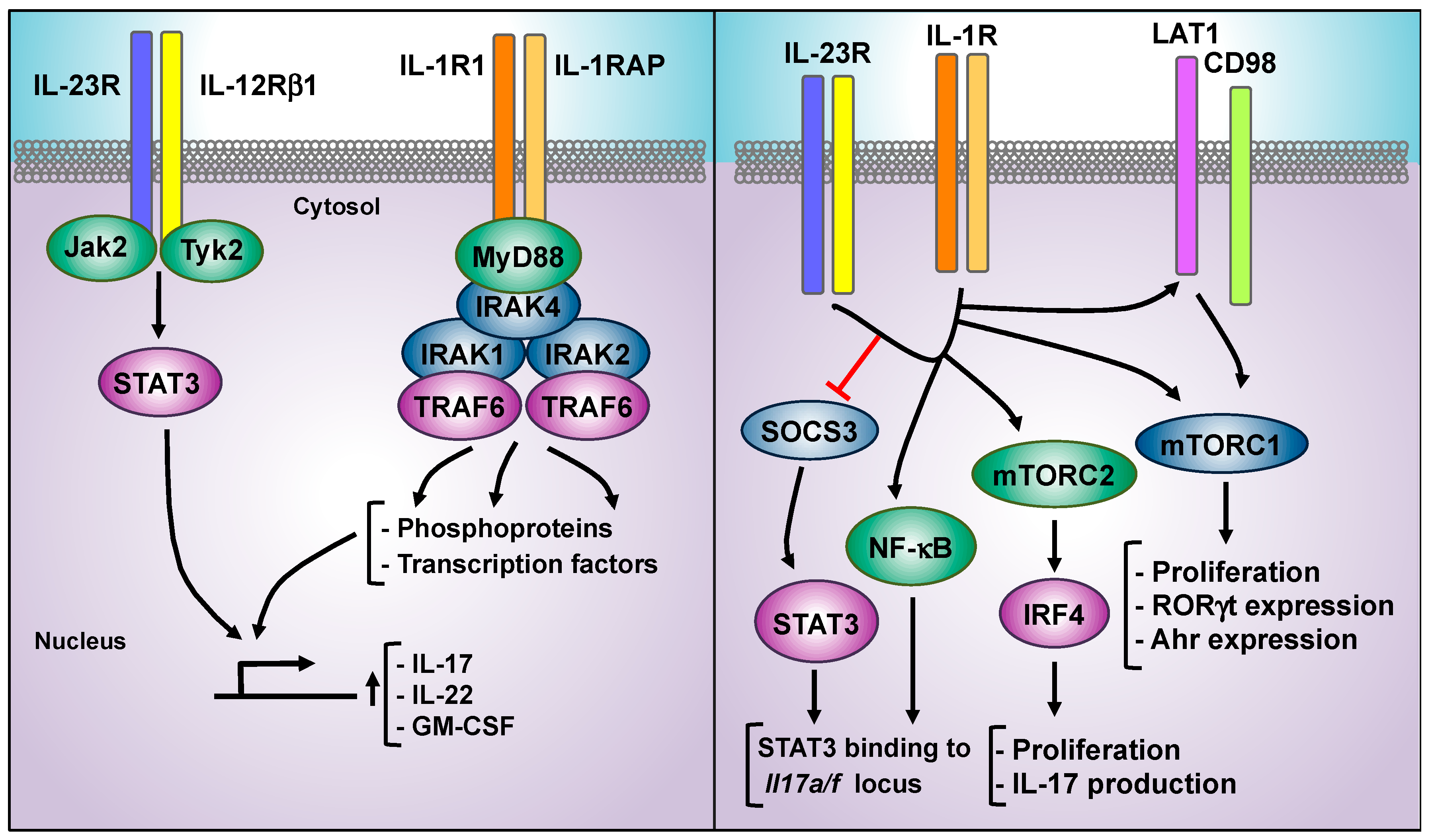



Cells Free Full Text Decoding Il 23 Signaling Cascade For New Therapeutic Opportunities Html
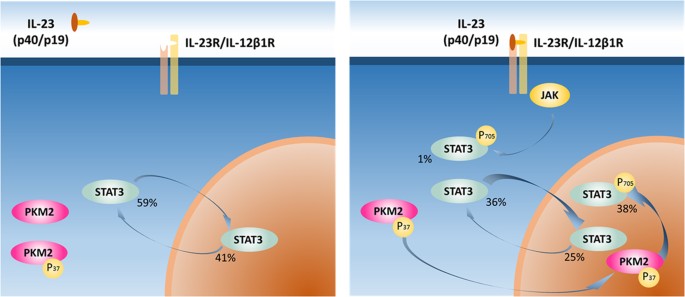



Integrative Phosphoproteomics Links Il 23r Signaling With Metabolic Adaptation In Lymphocytes Scientific Reports




Estrogen And Progesterone Decrease Let 7f Microrna Expression And Increase Il 23 Il 23 Receptor Signaling And Il 17a Production In Patients With Severe Asthma Journal Of Allergy And Clinical Immunology




A Cytokine Network Involving Il 36g Il 23 And Il 22 Promotes Antimicrobial Defense And Recovery From Intestinal Barrier Damage Pnas




A Receptor For The Heterodimeric Cytokine Il 23 Is Composed Of Il 12rb1 And A Novel Cytokine Receptor Subunit Il 23r The Journal Of Immunology




The Role Of Il 23 Receptor Signaling In Inflammation Mediated Erosive Autoimmune Arthritis And Bone Remodeling Razawy 18 European Journal Of Immunology Wiley Online Library




Interleukin 23 A New Atherosclerosis Target Journal Of Interferon Cytokine Research
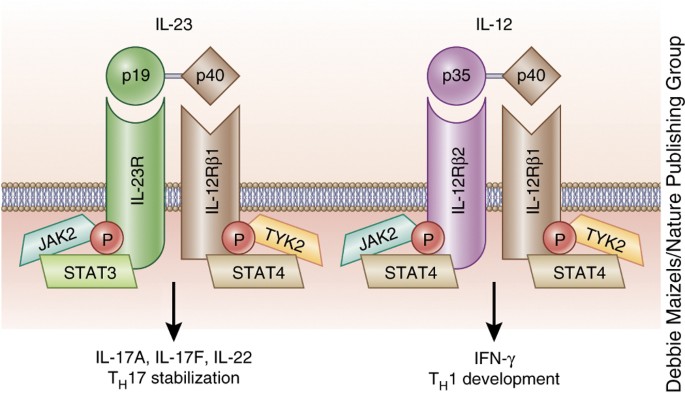



Il 12 And Il 23 Cytokines From Discovery To Targeted Therapies For Immune Mediated Inflammatory Diseases Nature Medicine




Discovery Of The Il 23 Il 17 Signaling Pathway And The Treatment Of Psoriasis The Journal Of Immunology




Interleukin Il 23 And Il 12 Composition Of The Il 23 And Il 12 Download Scientific Diagram




A Cytokine Network Involving Il 36g Il 23 And Il 22 Promotes Antimicrobial Defense And Recovery From Intestinal Barrier Damage Pnas
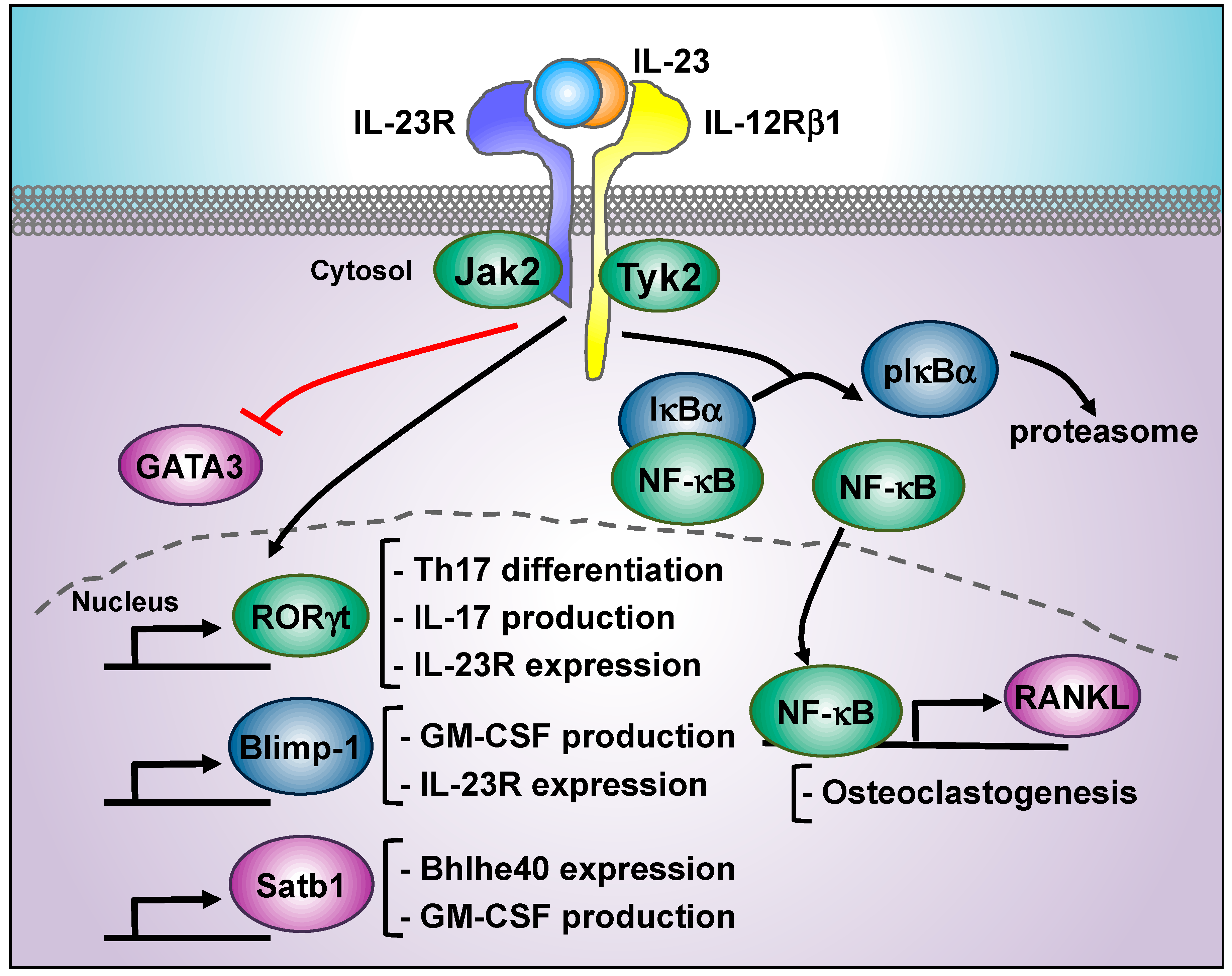



Cells Free Full Text Decoding Il 23 Signaling Cascade For New Therapeutic Opportunities Html




T Cell Intrinsic Prostaglandin E Sub 2 Sub Ep2 Ep4 Signaling Is Critical In Pathogenic T Sub H Sub 17 Cell Driven Inflammation Abstract Europe Pmc
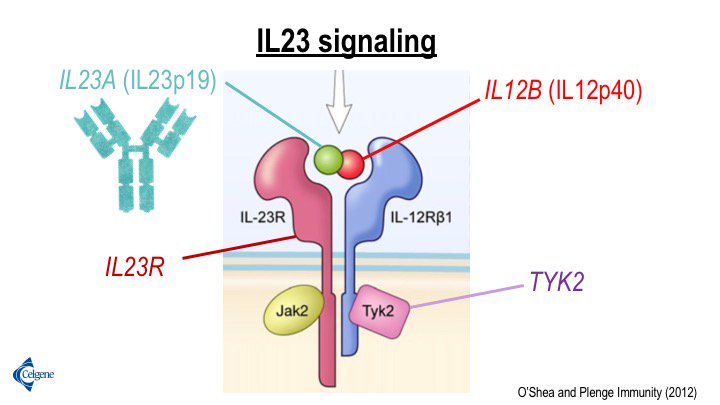



Robert Plenge The Il23 Signaling Pathway In Psoriasis Has Particular Strong Genetic Support Both Subunits Of The Il23 Ligand One Subunit Of The Il23 Receptor And Multiple Intracellular Signaling Molecules




Figure 1 From The Il 23 Il 17 Axis In Psoriatic Arthritis Semantic Scholar




Interleukin 23 Wikipedia
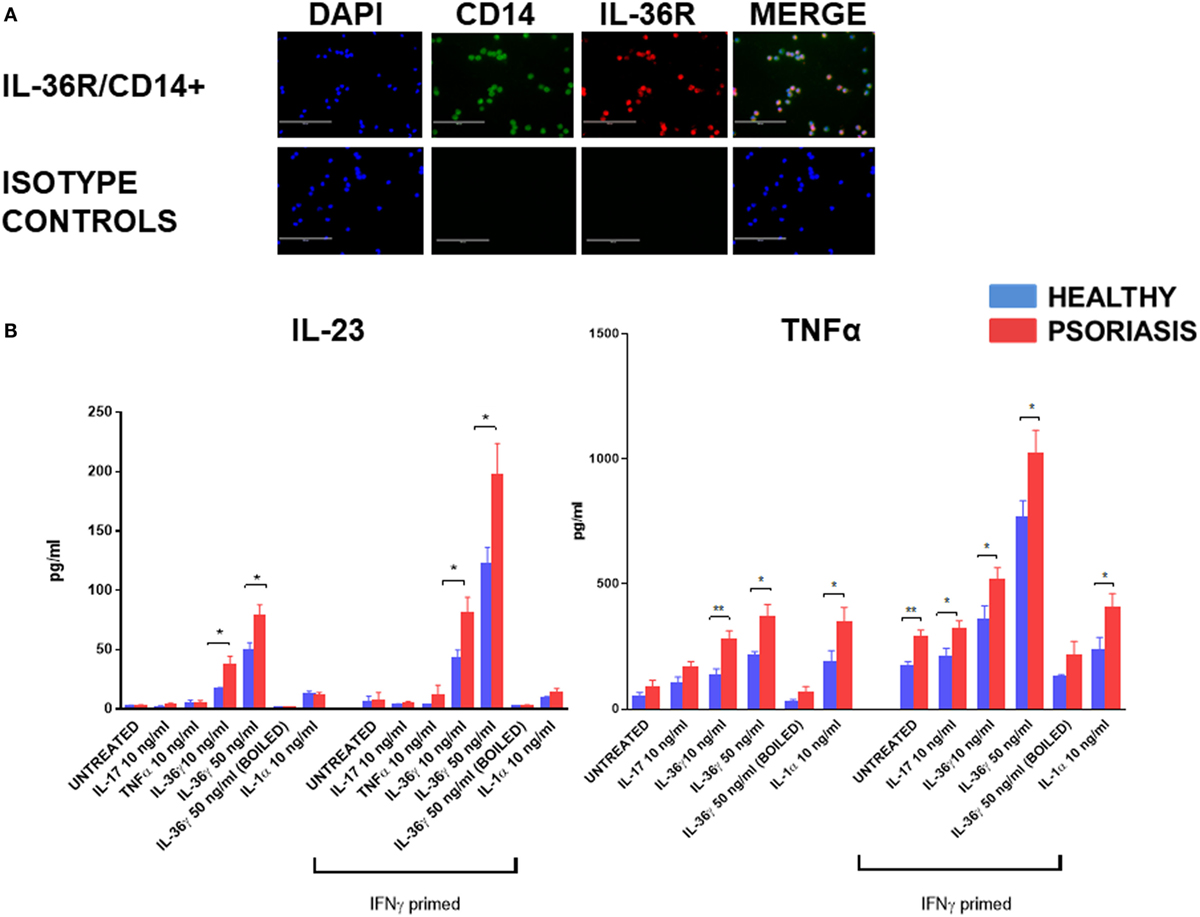



Frontiers Il 36g Is A Strong Inducer Of Il 23 In Psoriatic Cells And Activates Angiogenesis Immunology
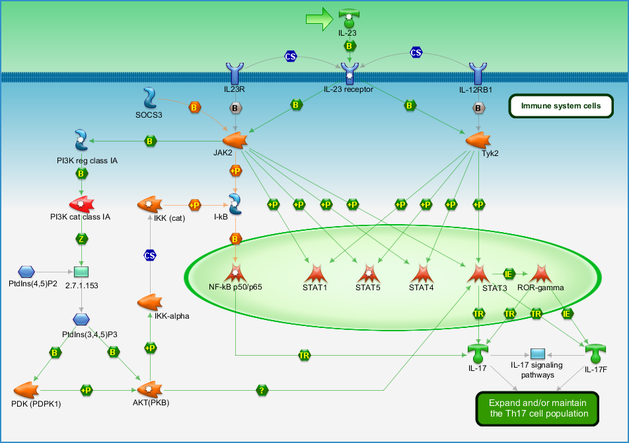



Immune Response Il 23 Signaling Pathway Pathway Map Primepcr Life Science Bio Rad




Th17 Cell Pathway In Human Immunity Lessons From Genetics And Therapeutic Interventions Immunity




Interleukin 12 Il 12 And Il 23 Signal Transduction Pathways Il 12 Download Scientific Diagram




A Cytokine Network Involving Il 36g Il 23 And Il 22 Promotes Antimicrobial Defense And Recovery From Intestinal Barrier Damage Pnas




The Il 23 Axis Genes Associationed With Psoriasis Il 12 And Il 23 Share Download Scientific Diagram




Pathophysiology And Inhibition Of Il 23 Signaling In Psoriatic Arthritis A Molecular Insight Sciencedirect




Stat3 And Nf Kb Signal Pathway Is Required For Il 23 Mediated Il 17 Production In Spontaneous Arthritis Animal Model Il 1 Receptor Antagonist Deficient Mice The Journal Of Immunology
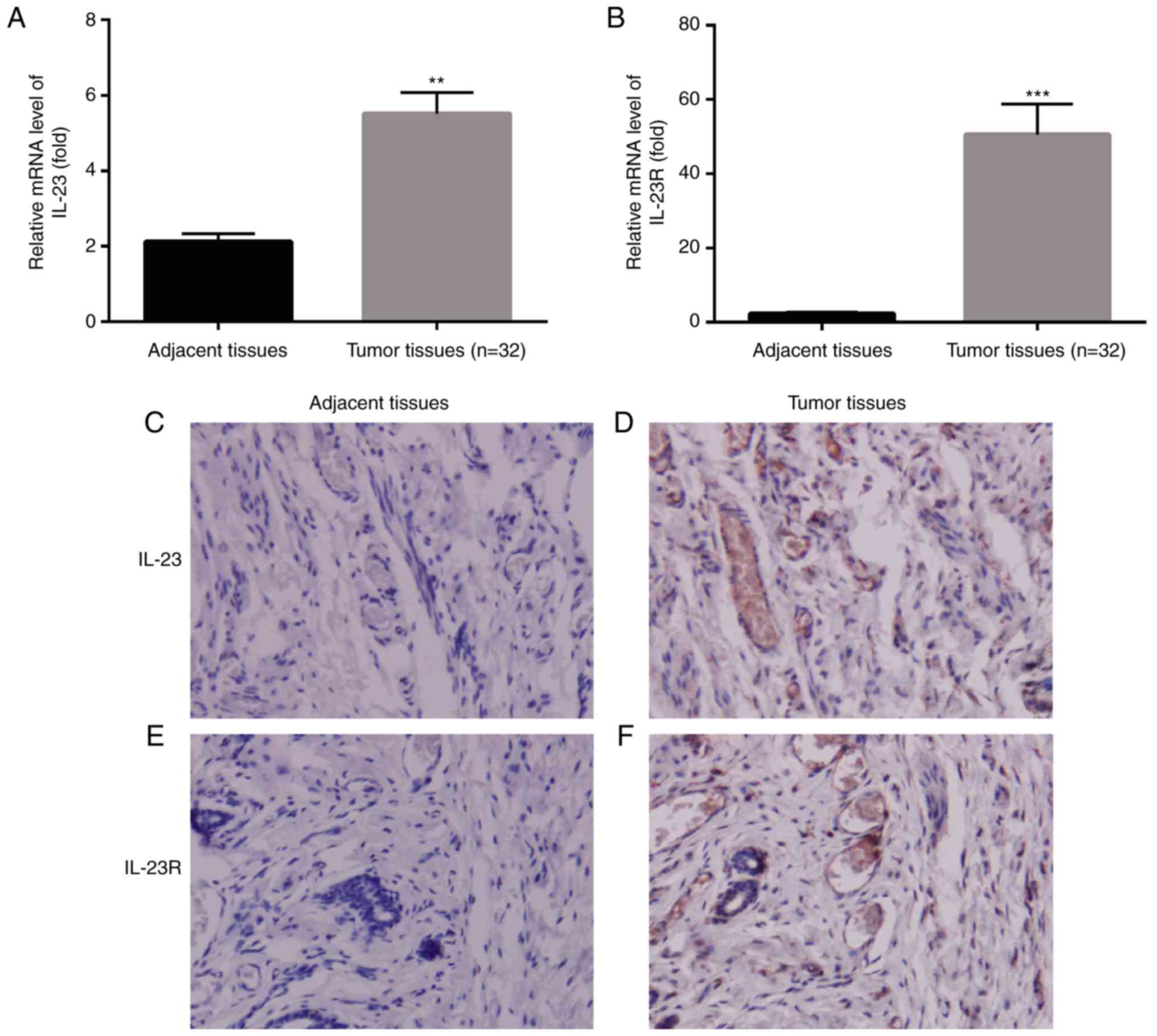



Aberrant Expression Of Il 23 Il 23r In Patients With Breast Cancer And Its Clinical Significance
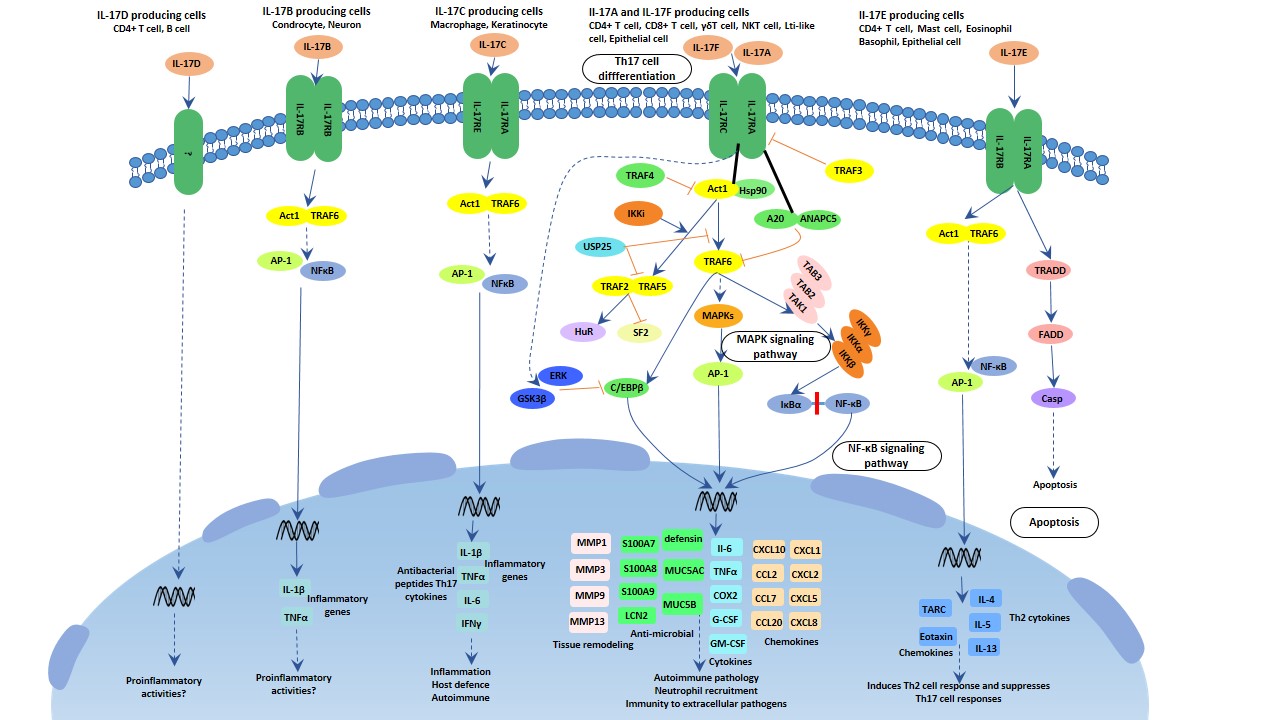



The Overview Of Interleukin




Epithelial Il 23r Signaling Licenses Protective Il 22 Responses In Intestinal Inflammation Topic Of Research Paper In Biological Sciences Download Scholarly Article Pdf And Read For Free On Cyberleninka Open Science Hub




Structural Activation Of Pro Inflammatory Human Cytokine Il 23 By Cognate Il 23 Receptor Enables Recruitment Of The Shared Receptor Il 12rb1 Sciencedirect




Il 23 Signaling Pathway Il 23 Is A Heterodimeric Cytokine Composed Of Download Scientific Diagram



Il 23 Signaling Regulation Of Pro Inflammatory T Cell Migration Uncovered By Phosphoproteomics




Morphine Inhibits Murine Dendritic Cell Il 23 Production By Modulating Toll Like Receptor 2 And Nod2 Signaling Journal Of Biological Chemistry



Il 23 Signaling Regulation Of Pro Inflammatory T Cell Migration Uncovered By Phosphoproteomics
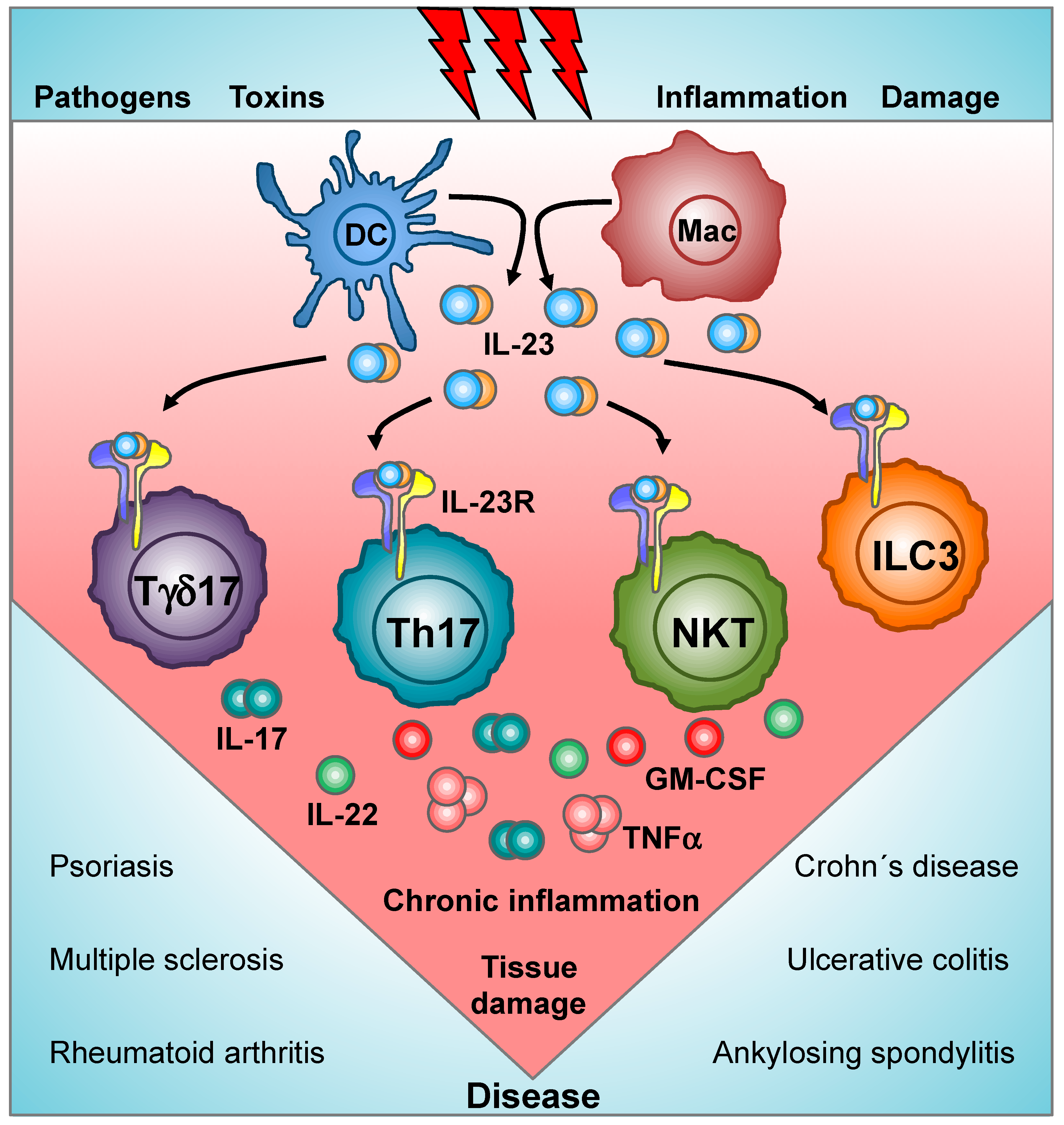



Cells Free Full Text Decoding Il 23 Signaling Cascade For New Therapeutic Opportunities
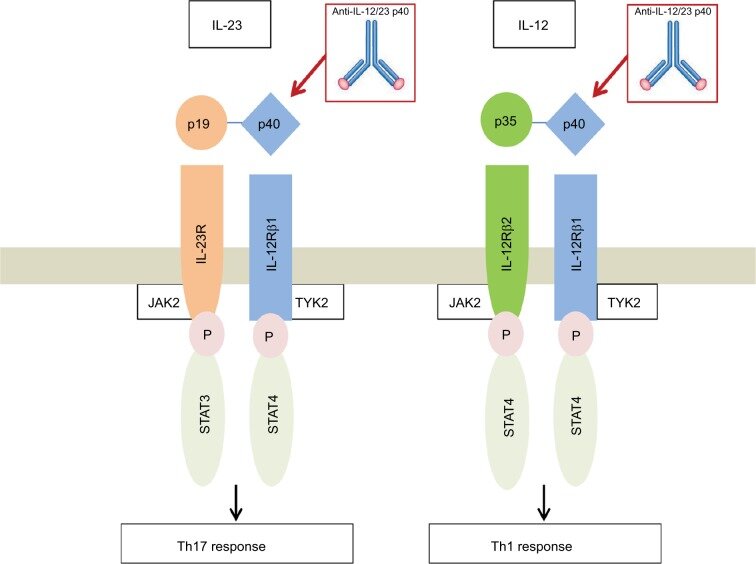



Schematic Representation Of Il 12 And Il 23 With Their Receptors And Download Scientific Diagram




Il 17 Signaling The Yin And The Yang Trends In Immunology
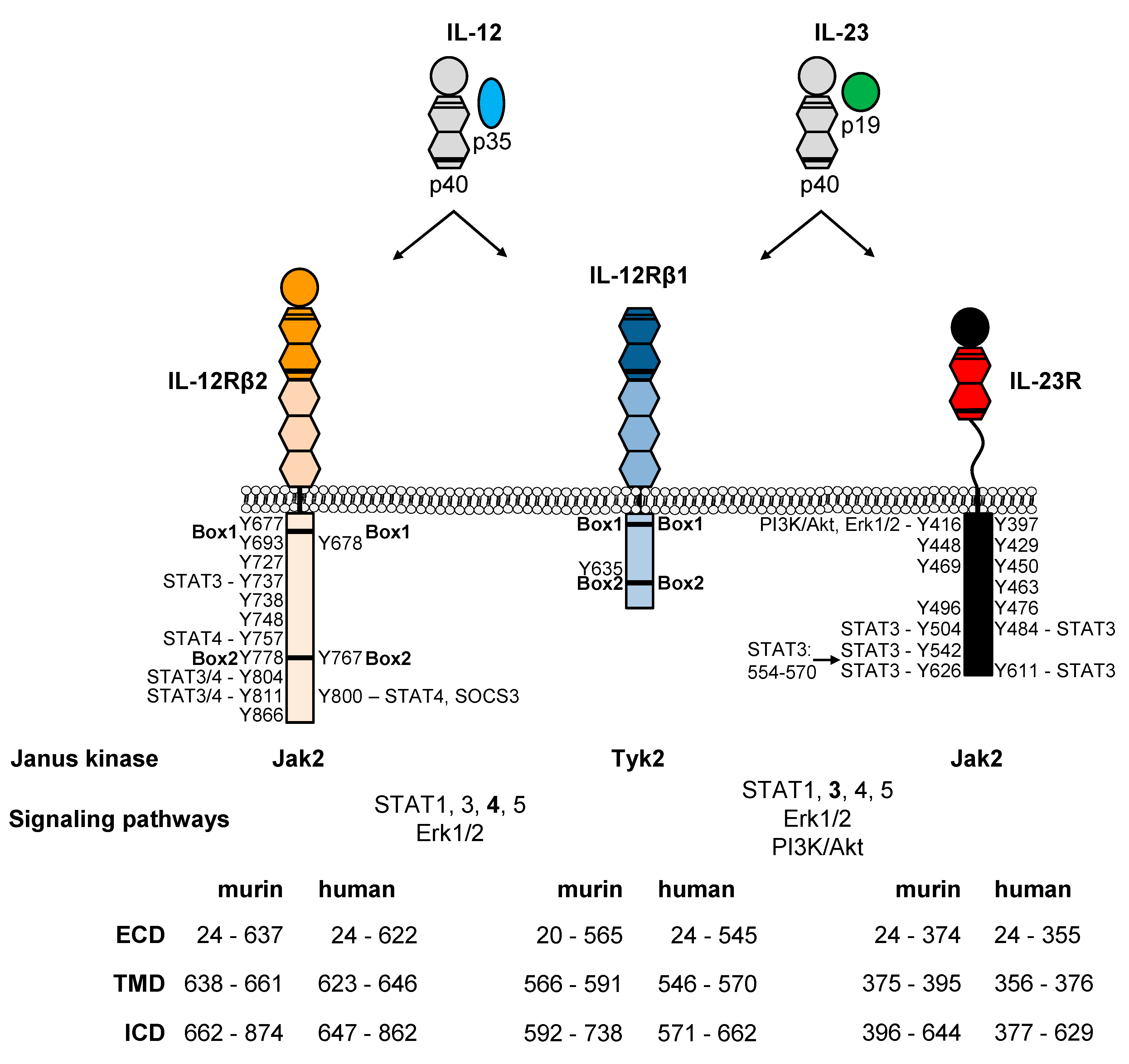



Cells Free Full Text Il 12 And Il 23 Close Relatives With Structural Homologies But Distinct Immunological Functions Html




Epithelial Il 23r Signaling Licenses Protective Il 22 Responses In Intestinal Inflammation Sciencedirect
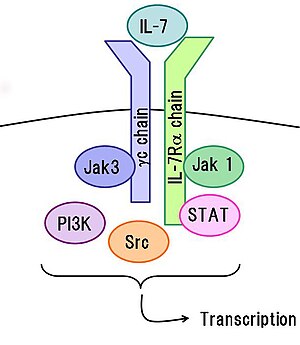



Interleukin 7 Wikipedia




Regulation Of The Il 23 And Il 12 Balance By Stat3 Signaling In The Tumor Microenvironment Abstract Europe Pmc




Identification Of Canonical Tyrosine Dependent And Non Canonical Tyrosine Independent Stat3 Activation Sites In The Intracellular Domain Of The Interleukin 23 Receptor Journal Of Biological Chemistry
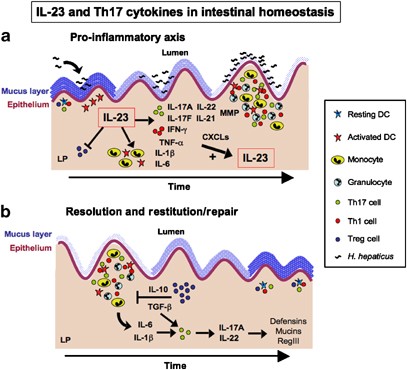



Il 23 And Th17 Cytokines In Intestinal Homeostasis Mucosal Immunology



Il 23 Signaling Regulation Of Pro Inflammatory T Cell Migration Uncovered By Phosphoproteomics
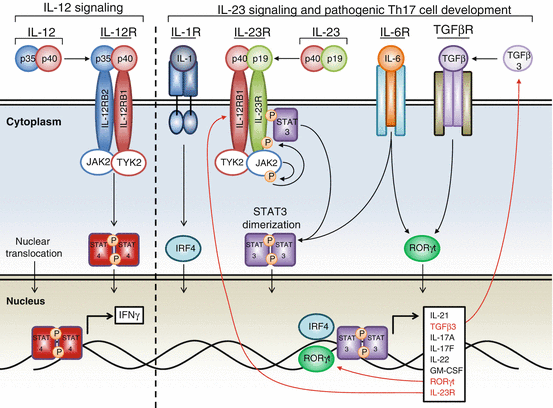



Il 23 In Health And Disease Springerlink




Inflammatory Disease Protective R381q Il23 Receptor Polymorphism Results In Decreased Primary Cd4 And Cd8 Human T Cell Functional Responses Pnas
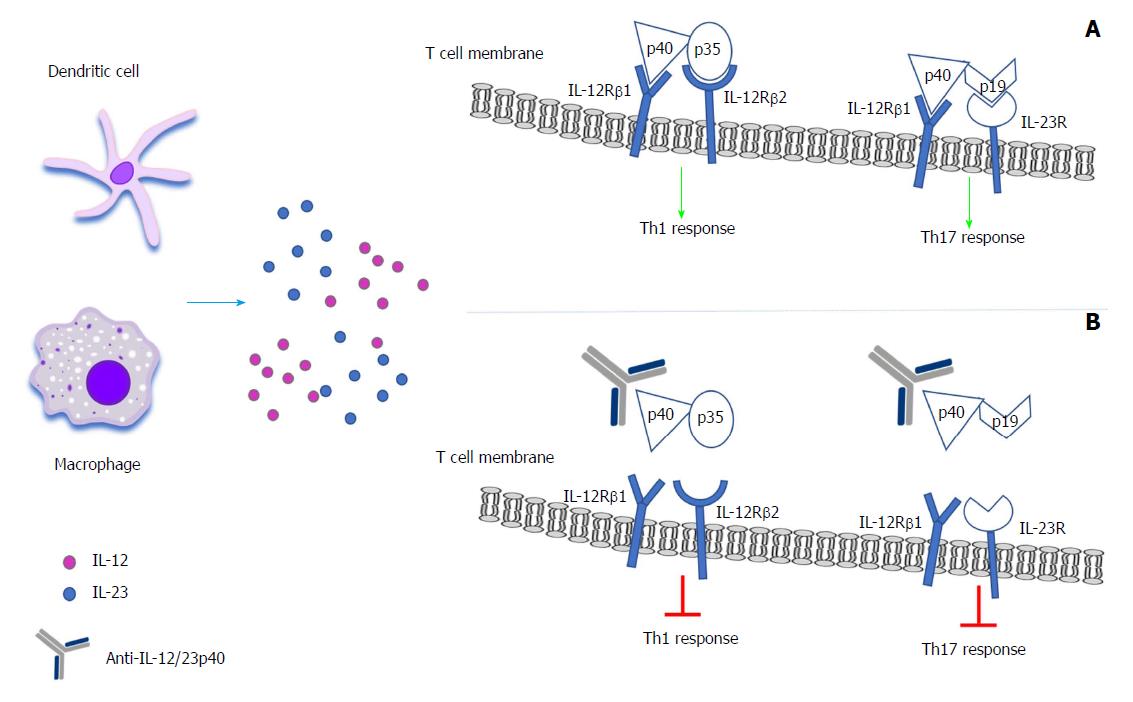



Interleukin 12 Interleukin 23 Pathway Biological Basis And Therapeutic Effect In Patients With Crohn S Disease




Il23 Receptor Protein Overview Sequence Structure Function And Protein Interaction Sino Biological




Structural Basis For Il 12 And Il 23 Receptor Sharing Reveals A Gateway For Shaping Actions On T Versus Nk Cells Sciencedirect




Interleukin 23 Promotes A Distinct Cd4 T Cell Activation State Characterized By The Production Of Interleukin 17 Journal Of Biological Chemistry




The Role Of Il 23 Receptor Signaling In Inflammation Mediated Erosive Autoimmune Arthritis And Bone Remodeling Razawy 18 European Journal Of Immunology Wiley Online Library
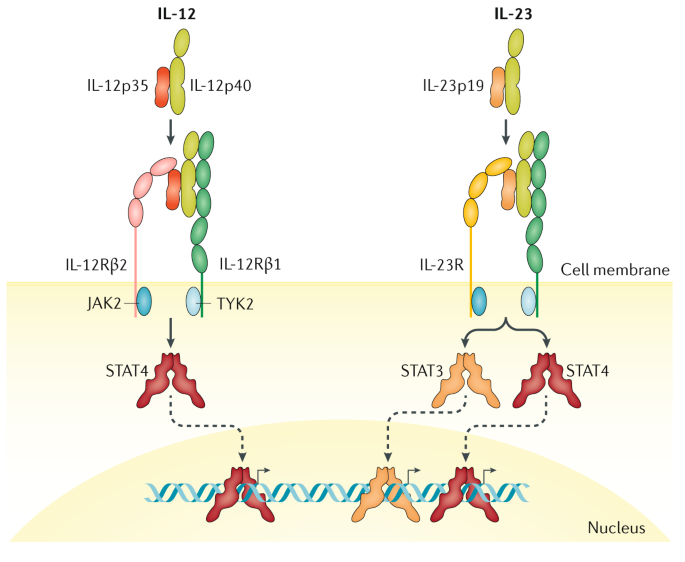



Il 12 Il 23 And Il 17 In Ibd Immunobiology And Therapeutic Targeting Nature Reviews Gastroenterology Hepatology




The Role Of Il 23 Receptor Signaling In Inflammation Mediated Erosive Autoimmune Arthritis And Bone Remodeling Razawy 18 European Journal Of Immunology Wiley Online Library
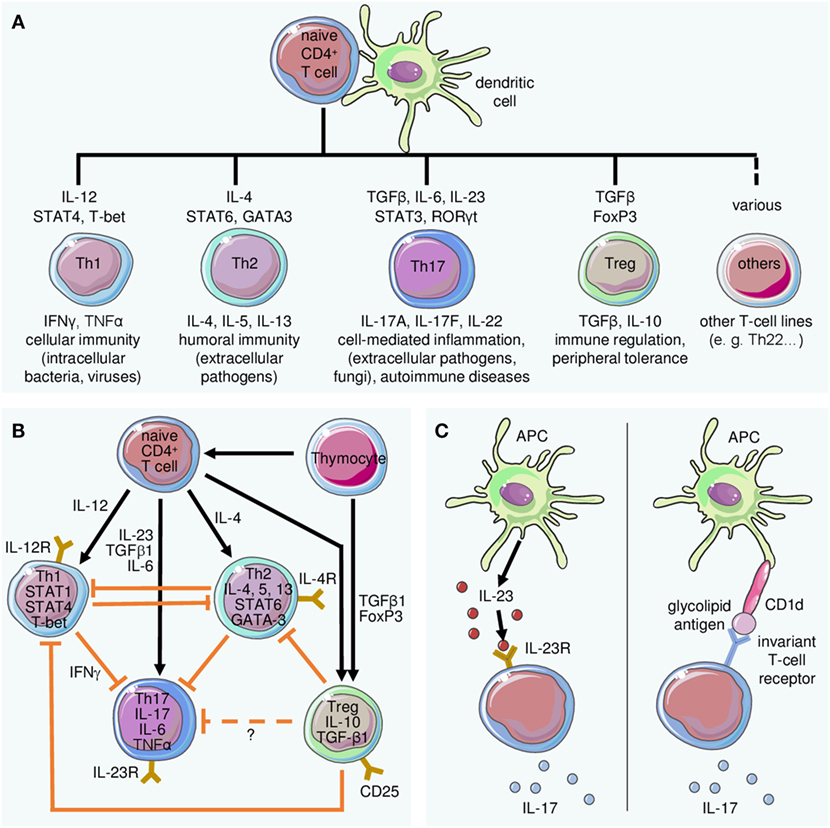



Frontiers The Interleukin 23 Interleukin 17 Axis Links Adaptive And Innate Immunity In Psoriasis Immunology
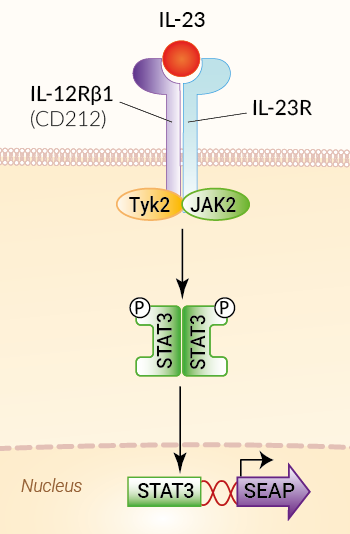



Hek Blue Il 23 Cells Il 23 Reporter Cells Invivogen




A Balance Of Interleukin 12 And 23 In Cancer Trends In Immunology




Il 12 Family Cytokines Receptors And Signaling Pathways Il 12 Download Scientific Diagram
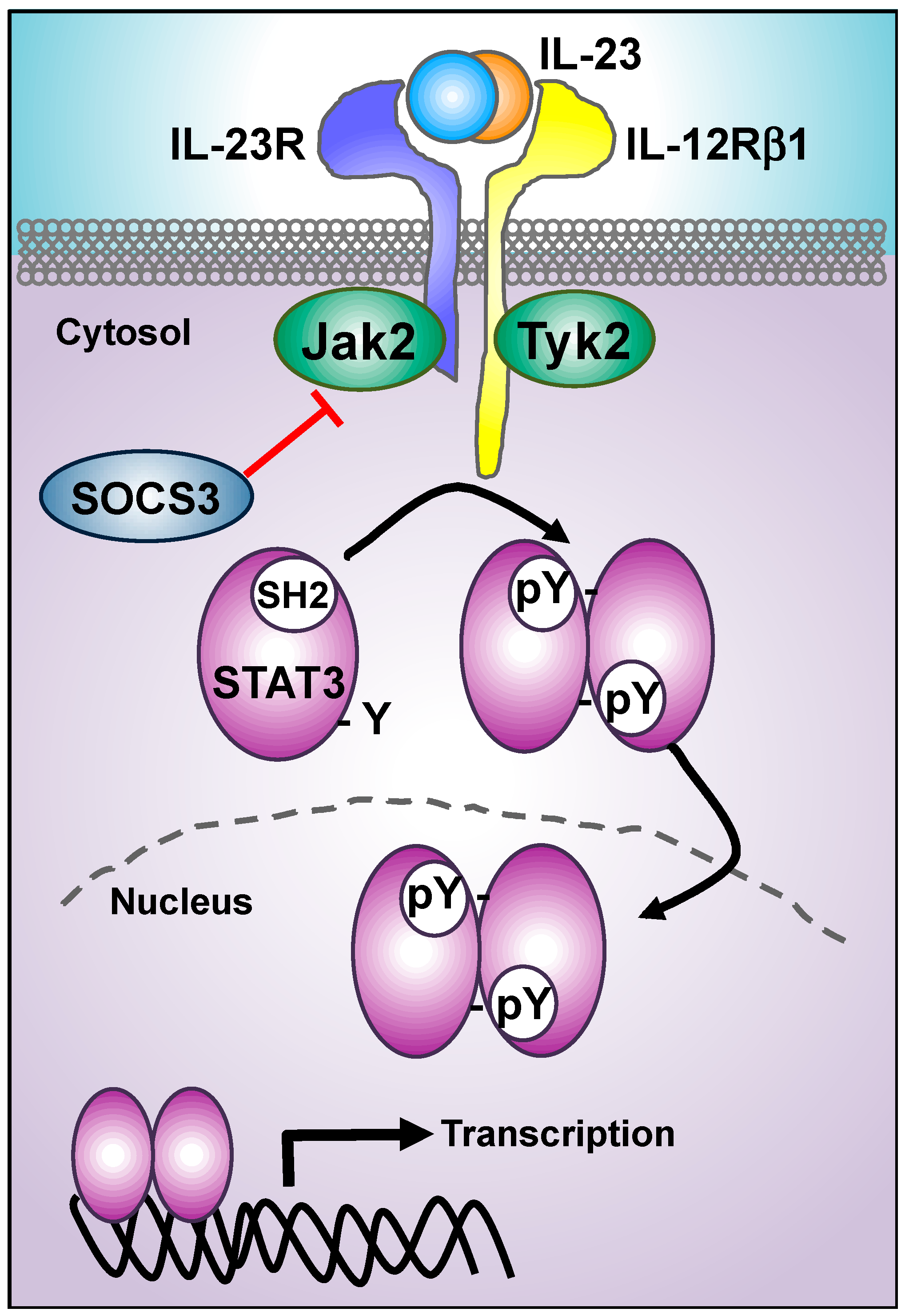



Cells Free Full Text Decoding Il 23 Signaling Cascade For New Therapeutic Opportunities Html




Discovery Of The Il 23 Il 17 Signaling Pathway And The Treatment Of Psoriasis The Journal Of Immunology




Therapeutics Targeting The Il 23 And Il 17 Pathway In Psoriasis The Lancet



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿